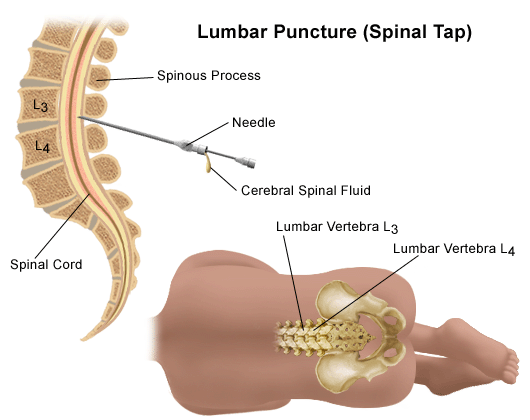
A lumbar puncture is a procedure to collect and look at the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Key points to remember
- a lumbar puncture is a procedure to see if there are cancer cells in the fluid that cushions the brain and spinal cord
- it is sometimes called a spinal tap
- most lumbar punctures happen while your child is asleep
- if your child has a temperature of 38 degrees Celsius or higher after the procedure, phone the hospital straightaway
What is a lumbar puncture?
A lumbar puncture (also called a spinal tap) is a procedure to see if there are cancer cells in the fluid that cushions the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid or CSF.
With some cancers, such as leukaemia or lymphoma, cancer cells can pass into the brain and the CSF. To find out whether this has happened, a doctor or nurse will remove a few drops of fluid by putting a thin needle between 2 bones in the spine.
What to expect
During the procedure, your child will lie on their side with their chin tucked to their chest and knees pulled up. In some cases, children can sit up and curl their back by tucking their chin to their chest.
When the back is in a curved position, a doctor or nurse will put a needle between the bones of the spine (vertebrae). The doctor or nurse will draw out the spinal fluid into a tube and send it to the laboratory for testing. For some types of cancer, chemotherapy goes through the same needle after removal of the spinal fluid.
Most lumbar punctures happen under general anaesthetic, so your child will be asleep and will not feel anything or be aware of the procedure.
After the procedure
The anaesthetist or another doctor will arrange medicine for any soreness afterwards. Some older children may choose to stay awake during a lumbar puncture. If your child wants to stay awake, they can have a local anaesthetic to help minimise discomfort.
Occasionally children get a headache after a lumbar puncture, but it is not common. If this happens, the anaesthetist or another doctor will arrange medicine to relieve it. There is less chance of a headache happening if your child can lie down for 2 hours after the procedure. Sometimes there can be a small amount of bleeding from the needle prick, but again this is not common.
The nurse will change the dressing and show how to press on the area to stop the bleeding. Infections can sometimes start in the needle prick area. Your nurse will talk to you about how to avoid this happening.
Before going home, the nurse will give instructions about removing the dressing.
Care at home
Take the dressing off 24 hours after the procedure. Follow the directions your nurse gave you in hospital.
Phone the hospital straightaway and tell the doctor or nurse on the ward if you notice any of these in the needle prick area:
- redness
- heat (feels warmer than skin in other parts of the body)
- fluid oozing out
Take your child's temperature if you are in any way concerned. If it is 38 degrees Celsius or higher, phone the hospital straightaway and tell the doctor or nurse on the ward. If your child needs pain relief, follow the instructions your nurse gave you in hospital.
Click Donate to fund the ongoing development of the Circulating Tumor DNA project which will improve outcomes for those children already diagnosed with cancer.
Disclaimer - Content on this blog is for educational use only. Please consult your doctor or other health professional to make sure the information is right for your child.
Copyright - Please note that the information on this blog is copyright owned by The Paediatric Society of New Zealand and Starship Foundation. See copyright information at the Kids Health website.